Are you a psychologist or social worker looking for effective tools to help your clients overcome addiction? Imagine a therapeutic approach that addresses the underlying psychological causes of addiction, helping clients break free from their dependencies and lead healthier lives.
Hypnotherapy, particularly Cognitive Hypnotic Psychotherapy, offers such a solution. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover how hypnotherapy can transform addiction treatment, explore key techniques, and learn practical steps to integrate these methods into your practice.
Understanding Addiction
What is Addiction?
Addiction is characterized by compulsive behaviors that individuals find difficult to control despite harmful consequences. It can manifest as substance addiction (e.g., alcohol, drugs) or behavioral addiction (e.g., gambling, internet use). Symptoms include cravings, compulsions, inability to stop, and significant lifestyle disruptions.
Psychological Layers of Addiction
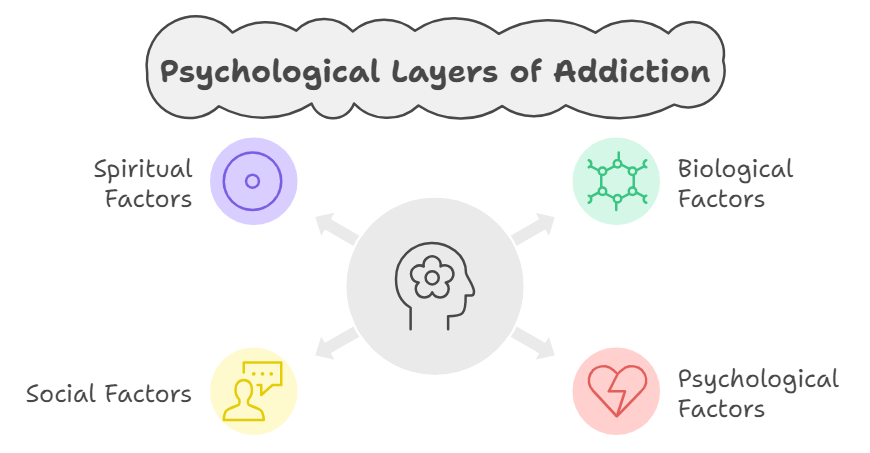

Addiction is influenced by multiple psychological layers:
- Biological:
- Genetic Predisposition: Genetic factors can make individuals more susceptible to addiction.
- Brain Chemistry: Addictive substances and behaviors alter brain chemistry, creating dependencies.
- Psychological:
- Emotional Distress: Individuals may use substances or behaviors to cope with emotional pain or stress.
- Unresolved Traumas: Past traumas can lead to addictive behaviors as a form of self-medication.
- Mental Health Disorders: Co-occurring mental health issues like anxiety or depression often contribute to addiction.
- Social:
- Peer Pressure: Social circles can influence the initiation and continuation of addictive behaviors.
- Family Dynamics: Dysfunctional family relationships can contribute to the development of addiction.
- Societal Influences: Societal norms and media portrayal of substance use can impact addiction.
- Spiritual:
- Sense of Emptiness: A lack of purpose or spiritual fulfillment can lead individuals to seek solace in addictive behaviors.
- Existential Crises: Questions about life’s meaning and purpose can drive individuals toward addiction.
Hypnotherapy for Addiction
How Hypnotherapy Works
Hypnotherapy is a state of focused awareness or trance where individuals are more receptive to suggestions. This state can be utilized to address the underlying causes of addiction and facilitate positive behavioral changes.

Cognitive Hypnotic Psychotherapy
Cognitive Hypnotic Psychotherapy (CHP) is an integrative approach that uses hypnosis as a base to seamlessly integrate different approach of psychotherapy. It aims to address both the conscious and subconscious mind, enabling clients to achieve deep, lasting change.
By focusing on the root causes of addiction, CHP helps clients reframe negative patterns, manage triggers, and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Key Techniques in Cognitive Hypnotic Psychotherapy
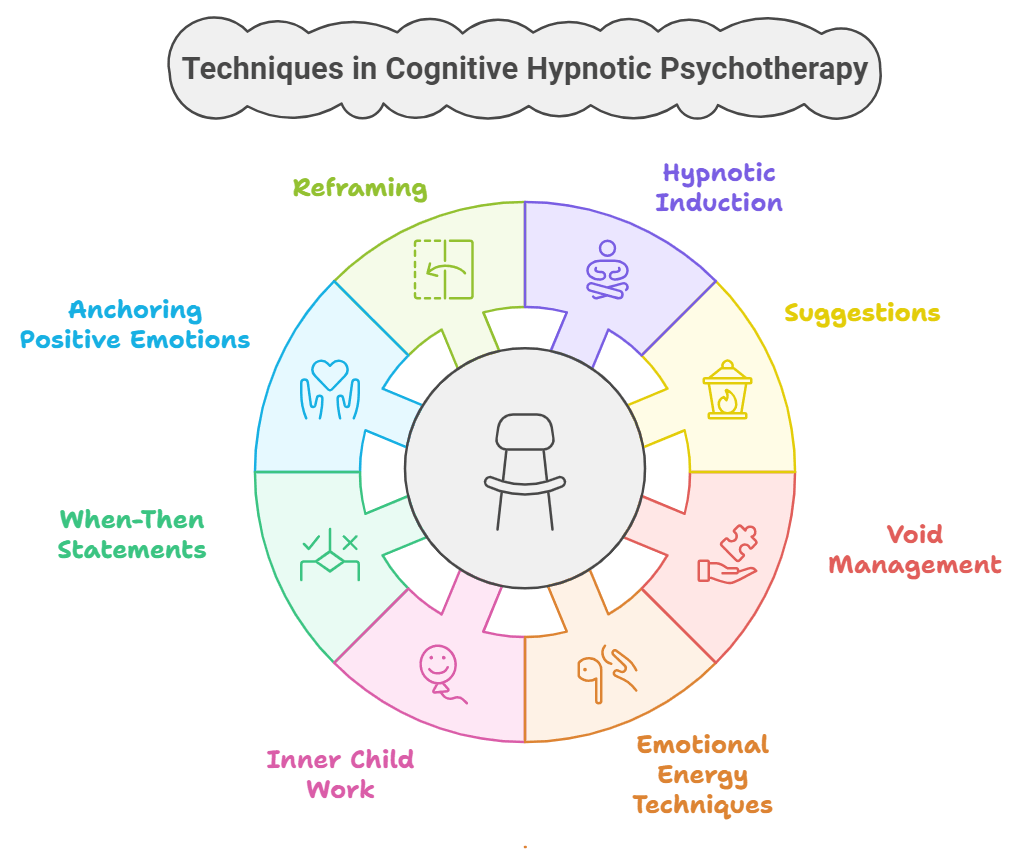
- Hypnotic Induction and Deepening:
- Techniques to guide the client into a deep, relaxed state of focus.
- This state increases suggestibility and reduces critical thinking barriers.
- Suggestions:
- Carefully crafted phrases that influence the subconscious mind.
- Used to reinforce positive behaviors and diminish addictive tendencies.
- Void Management:
- Identification: Identify the void or unmet needs driving the addictive behavior.
- Hypnotherapy Techniques: Use hypnotherapy to explore these voids, understand their origins, and find healthy alternatives to fill them.
- Example: For someone with an alcohol addiction due to loneliness, hypnotherapy can help them develop a sense of connection through social activities or hobbies.
- Emotional Energy Techniques (EET):
- Helps manage intense emotions that surface during therapy.
- Techniques like tapping or guided visualization to release emotional blockages.
- Inner Child Work:
- Addresses deep-seated emotional wounds from childhood.
- Reframes past experiences to foster healing and reduce reliance on addictive behaviors.
- When-Then Statements:
- Cognitive restructuring to handle triggers.
- “When I feel stressed, then I will take deep breaths instead of smoking.”
- Anchoring Positive Emotions:
- Anchoring techniques to evoke positive emotions in triggering situations.
- Helps clients feel calm and in control.
- Reframing:
- Identifying and altering the positive intention behind the addictive behavior.
- Replacing harmful habits with healthier alternatives.
Practical Steps and Case Study: Ajay’s Journey to Overcome Alcohol Addiction
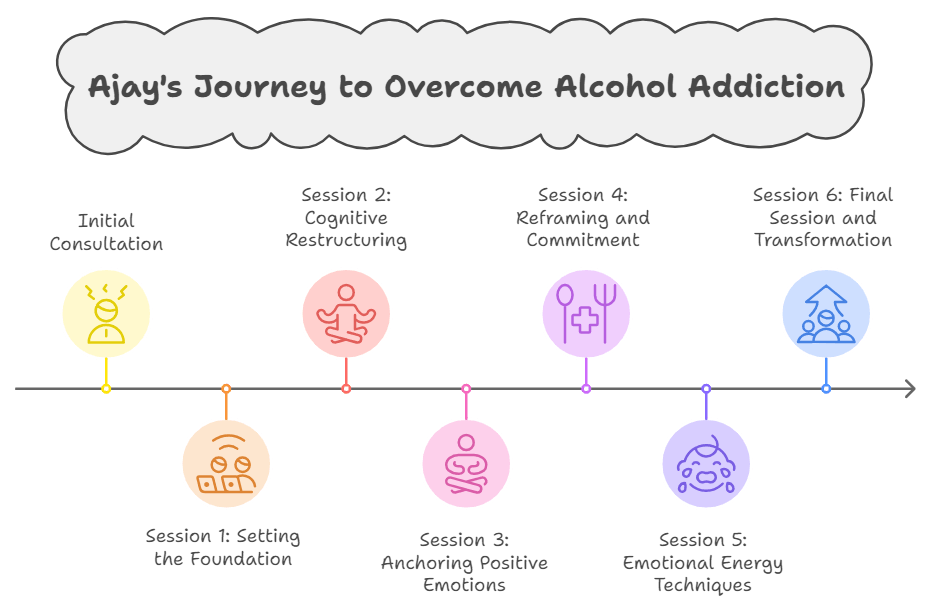
Ajay, a 35-year-old man, sought hypnotherapy to quit his alcohol addiction. He started drinking heavily during a financial crisis and felt unable to stop, despite the negative impact on his health and family life. Here’s a step-by-step look at Ajay’s therapy process:
Initial Session: Building Rapport and Understanding the Problem
- Initial Consultation:
- Ajay explains his struggle with alcohol and its effects on his health and relationships.
- He defines his desired outcome: to quit drinking and improve his life.
Session 1: Setting the Foundation
- Recap and Clarification:
- Review the previous session and confirm Ajay’s goals.
- Ajay wishes to quit drinking and maintain his health.
- Future Visualization:
- Guide Ajay to imagine a future free from addiction.
- Assign homework: Write down future goals and desired feelings.
Session 2: Cognitive Restructuring
- Review Homework and Triggers:
- Discuss Ajay’s future goals and identify specific triggers.
- Ajay identifies stress as a major trigger for drinking.
- When-Then Technique:
- Help Ajay develop new responses to triggers.
- Example: “When I feel stressed, then I will go for a walk.”
Session 3: Anchoring Positive Emotions
- Recap and Emotional Anchoring:
- Review progress and introduce anchoring techniques.
- Ajay recalls a calm moment from the past and anchors this feeling for future use.
Session 4: Reframing and Commitment to New Behavior
- Reframing Technique:
- Identify the positive intention behind Ajay’s drinking.
- Replace harmful habits with healthier alternatives.
- Ajay commits to healthier stress management techniques.
Session 5: Emotional Energy Techniques (EET) and Inner Child Work
- EET for Intense Emotions:
- Use Emotional Energy Techniques to manage any intense emotions that arise.
- Use delayering to find the root cause driving the .
- Inner Child Work:
- Address deep-seated emotional wounds from Ajay’s childhood.
- Reframe past experiences to foster healing and reduce reliance on alcohol.
Session 6: Final Session and Transformation
- Review Progress and Transformational Techniques:
- Discuss Ajay’s improvements and use techniques like the Circle of Transformation.
- Ajay successfully reduces his alcohol intake, feeling calm and in control.
- Hypnotic Recording:
- Ajay is asked to listen to a customized hypnotic recording after the sessions for the next few weeks.
- This ensures that the changes are reinforced and strengthened.
Conclusion
Research supports the effectiveness of hypnotherapy in treating addiction. A 2007 study by the American College of Chest Physicians found that hypnotherapy significantly increased the likelihood of smoking cessation compared to other methods. By addressing the psychological layers of addiction and employing techniques from Cognitive Hypnotic Psychotherapy, therapists can help clients achieve lasting change.
If you are a therapist or psychologist and want to integrate these powerful techniques into your practice, consider exploring our internationally accredited program, “Cognitive Hypnotic Psychotherapy®“.
This program offers comprehensive training in advanced hypnotherapy techniques to enhance your ability to help clients overcome addiction and other challenges.

