Introduction
In the realm of psychological therapies, two methodologies stand out for their efficacy and widespread use: Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) and Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT).
NLP, rooted in the study of human behaviour, communication, and subjective experience, offers a range of techniques aimed at personal development and therapeutic intervention. On the other hand, CBT, grounded in cognitive psychology, focuses on identifying and modifying dysfunctional thoughts and behaviours to alleviate mental health conditions.

While both approaches aim to bring about positive changes in individuals, an intriguing question arises: Are NLP and CBT fundamentally similar or different?
This article delves into the core principles, techniques, similarities, differences, and potential integration of CBT and NLP to provide a comprehensive understanding of their relationship.
Understanding NLP
Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) is a psychological approach developed in the 1970s by Richard Bandler and John Grinder. At its core, NLP explores the relationships between neurology (neuro), language (linguistic), and patterns of behaviour (programming).
NLP posits that by understanding how individuals perceive the world and communicate internally and externally, one can facilitate positive changes in behaviour and thought patterns. Key techniques utilized in NLP include reframing, anchoring, and modeling.
Reframing involves changing the way an individual perceives a situation by altering the meaning attached to it. Anchoring associates a specific stimulus with a particular emotional state, allowing individuals to access desired states at will.
Modeling involves emulating the behaviours and thought processes of successful individuals to achieve similar outcomes. NLP finds applications in various domains, including therapy, coaching, business, and personal development.
Understanding CBT
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is a widely practiced therapeutic approach grounded in the principles of cognitive psychology. Developed by Aaron Beck in the 1960s, CBT aims to identify and modify dysfunctional thoughts and behaviours that contribute to psychological distress.
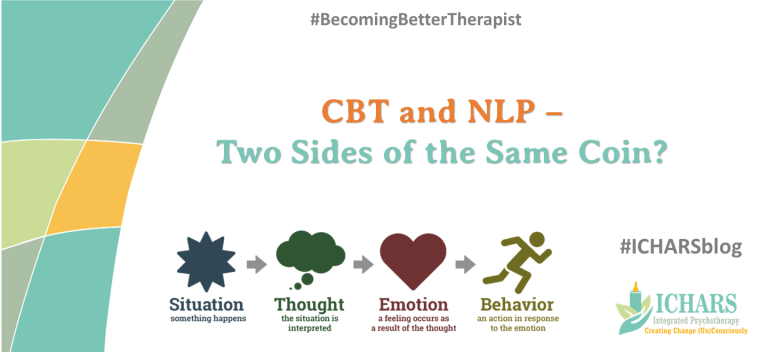
Central to CBT is the concept that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviours are interconnected and influence one another. By targeting maladaptive thoughts and behaviours through structured interventions, CBT seeks to alleviate symptoms of mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and trauma.
Common techniques covered in CBT Courses include cognitive restructuring, exposure therapy, and behavioural experiments.
- Cognitive restructuring involves challenging and replacing irrational or negative thought patterns with more adaptive ones.
- Exposure therapy exposes individuals to feared stimuli in a controlled environment to reduce anxiety or avoidance behaviours.
- Behavioural experiments involve testing the validity of beliefs or assumptions through real-life experiences.
CBT has been extensively researched and proven effective in treating a wide range of psychological disorders.
Comparing CBT and NLP
While NLP and CBT share some similarities, they also exhibit distinct differences in their theoretical foundations, approaches, and empirical support.
Similarities between CBT and NLP
- Focus on Changing Thoughts, Beliefs, and Behaviours:
Both emphasize the importance of identifying and modifying thoughts, beliefs, and behaviours that contribute to distress or dysfunction. By addressing cognitive processes and behavioural patterns, both approaches aim to facilitate positive changes in individuals. - Emphasis on the Importance of Language and Communication:
Both recognize the significant role of language and communication in shaping individual experiences and behaviours. Language is viewed as a powerful tool for reframing perceptions, challenging beliefs, and facilitating change in both approaches. - Incorporation of Goal-Setting and Problem-Solving Techniques:
Both employ goal-setting and problem-solving techniques to help individuals clarify their objectives, overcome obstacles, and achieve desired outcomes. By setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals, individuals are empowered to take proactive steps toward change.
Differences between NLP and CBT
- Theoretical Underpinnings and Origins:
NLP draws heavily from various disciplines, including linguistics, cognitive psychology, and systems theory, to develop its theoretical framework. In contrast, CBT is firmly rooted in cognitive psychology and behavioural principles, with a focus on empirical research and evidence-based practice. - Approach to Addressing and Treating Psychological Issues:
NLP employs a range of techniques aimed at facilitating rapid and profound change in individuals by accessing and modifying unconscious patterns of thought and behaviour. It often emphasizes subjective experiences, metaphorical language, and visualization techniques to evoke therapeutic outcomes.
In contrast, CBT follows a structured, goal-oriented approach that focuses on identifying and challenging specific cognitive distortions and behavioural patterns contributing to psychological distress. - Evidence Base and Empirical Support:
While CBT has accumulated a substantial body of empirical evidence supporting its efficacy in treating various mental health conditions, the empirical support for NLP is more limited and often controversial.
Critics argue that NLP lacks scientific rigor and empirical validation, relying instead on anecdotal evidence and subjective experiences to support its claims.
Integration of CBT and NLP
Despite their differences, there is potential for synergies between NLP and CBT that can enhance therapeutic outcomes and broaden the scope of interventions.
Exploration of Potential Synergies
Integrating NLP techniques, such as reframing and visualization, with CBT interventions can enhance the effectiveness of cognitive restructuring and exposure therapy. By incorporating NLP’s emphasis on language and communication, therapists can help clients reframe negative beliefs and develop more adaptive coping strategies.
Examples of Integration
For example, combining CBT’s cognitive restructuring techniques with NLP’s anchoring technique can help individuals associate positive emotions with challenging situations, making it easier to confront and reevaluate their beliefs.
Similarly, integrating NLP’s modeling technique with CBT’s behavioural experiments can facilitate experiential learning and behaviour change by providing clients with tangible examples of adaptive behaviours.
Challenges and Considerations
However, integrating NLP and CBT approaches requires careful consideration of ethical, theoretical, and practical considerations. Therapists must ensure that interventions are evidence-based, culturally sensitive, and tailored to the individual needs and preferences of clients.
Additionally, therapists should undergo comprehensive training and supervision to effectively integrate NLP techniques into their CBT practice.
Practical Implications and Applications
The integration of NLP and CBT has practical implications for therapists, practitioners, and individuals seeking therapy or personal development.
Implications for Therapists and Practitioners
Therapists and practitioners can expand their therapeutic toolkit by integrating NLP techniques into their CBT practice, thereby enhancing their ability to address a broader range of client issues and facilitate more profound therapeutic outcomes.
By combining the strengths of both approaches, therapists can offer more personalized and holistic interventions that resonate with clients’ unique needs and preferences.
Considerations for Individuals Seeking Therapy or Personal Development
Individuals seeking therapy or personal development can benefit from exploring the integration of NLP and CBT approaches to address their concerns effectively.
By working with therapists who are skilled in integrating NLP techniques into their CBT practice, individuals can access a wider range of therapeutic strategies and interventions tailored to their specific goals and preferences.
Future Directions and Research Opportunities
Future research should focus on examining the effectiveness and feasibility of integrating NLP and CBT approaches across different populations and settings. Longitudinal studies are needed to assess the long-term outcomes of integrated interventions and determine the mechanisms underlying therapeutic change.
Additionally, qualitative research can provide insights into clients’ experiences and perceptions of integrated CBT and NLP interventions, informing the development of best practices and guidelines for clinical practice.
Case Studies and Examples
To illustrate the potential benefits of integrating NLP and CBT approaches, consider the following case studies:
Case Study 1: Sarah, a 35-year-old woman struggling with social anxiety, seeks therapy to overcome her fear of public speaking. Her therapist integrates NLP anchoring techniques with CBT exposure therapy to help her associate feelings of confidence and relaxation with public speaking situations. Through repeated exposure and positive reinforcement, Sarah gains mastery over her anxiety and improves her public speaking skills.
Case Study 2: David, a 45-year-old man experiencing chronic pain, undergoes a multidisciplinary pain management program that integrates NLP visualization techniques with CBT pain coping skills. By visualizing himself engaged in enjoyable activities and using cognitive strategies to challenge pain catastrophizing, David experiences a reduction in pain intensity and improvement in physical functioning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while NLP and CBT exhibit both similarities and differences in their theoretical foundations, approaches, and empirical support, they can be viewed as complementary rather than opposing paradigms.
By integrating NLP techniques, such as reframing and anchoring, with CBT interventions, therapists can enhance the effectiveness of cognitive restructuring and exposure therapy, leading to more profound therapeutic outcomes.
However, the integration of NLP and CBT approaches requires careful consideration of ethical, theoretical, and practical considerations, as well as ongoing research to validate its efficacy and inform best practices.
Moreover, it’s important to recognize the potential for further integration by including hypnosis as well. In this sense, all three modalities – Hypnosis, CBT, and NLP – can be integrated to create a powerful change process.
Cognitive Hypnotic Psychotherapy™ Program offers a robust framework based on this integration, providing therapists and practitioners with a comprehensive toolkit to address a wide range of client issues effectively. By embracing the synergies between these modalities, therapists can offer more personalized and holistic interventions that empower individuals to achieve lasting positive change in their lives.