What is Operant Conditioning?
Operant Conditioning is a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behaviour in other words it is a type of learning in which an individual’s behaviour is modified by its consequences or the response the behaviour gets. The behaviour may change in form, frequency, or strength.
This term was coined by B.F Skinner who believed that we do have such a thing as a mind, but that it is simply more productive to study observable behaviour rather than internal mental events.
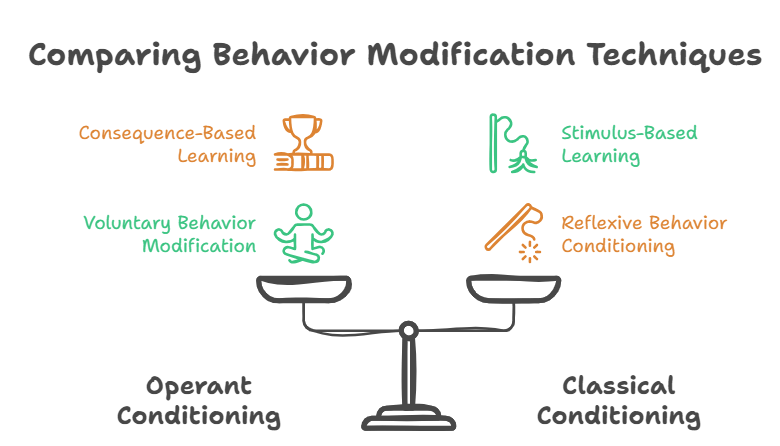
Operant vs Classical Conditioning
Operant conditioning attempts to modify behaviours which are generally voluntary in nature and can be maintained by consequences or responses as opposed to classic conditioning which deals with the conditioning of automatic or reflexive behaviour which is not maintained by consequences.
Types of Operants / Responses to a behaviour:
Skinner identified three types of responses or operants that can follow behaviour.
- Neutral operants are Responses from the environment that neither increase nor decrease the probability of a behaviour being repeated.
- Reinforcement that strengthens behaviour is a response or a consequence that causes a behaviour to occur with greater frequency. Reinforcers can be positive or negative.
- Punishment that weakens behaviour is a response or a consequence that causes a behaviour to occur with less frequency. Just like Reinforcements, there can be two types of punishment: positive and negative.
Core Tools of Operant Conditioning
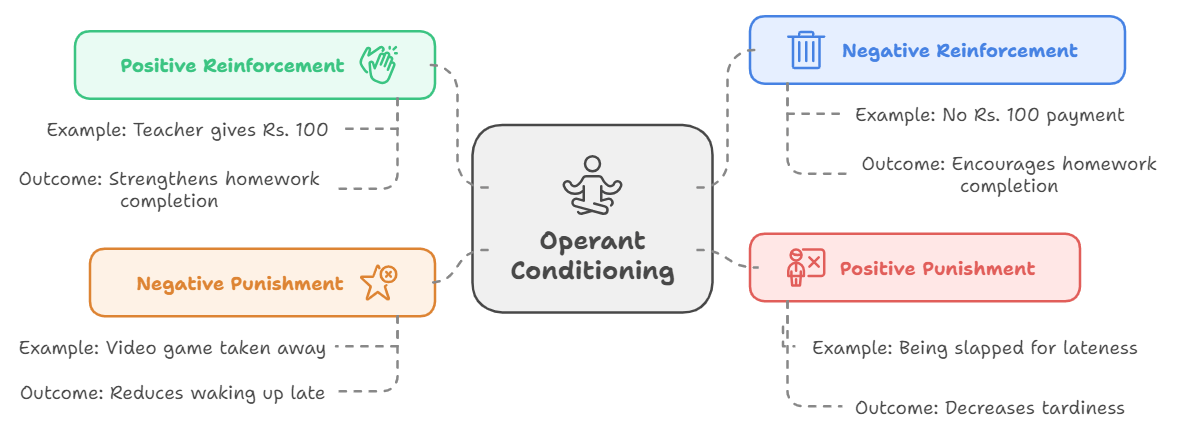
- Positive reinforcers are Favorable events or outcomes that are presented after the behaviour. This Positive reinforcement strengthens a behaviour by providing a consequence an individual finds rewarding. For example, if your teacher gives you Rs. 100 (reward) each time you complete your homework (behaviour) you are more likely to repeat this behaviour in the future, thus strengthening the behaviour of completing your homework.
- Negative reinforcers as a tool for operant conditioning involve the removal of unfavourable events or outcomes after the display of a behaviour. In these situations, a response is strengthened by the removal of something considered unpleasant.
For example, let us say, you have to give your teacher Rs. 100 every day (unfavourable outcome). But on the days you complete your homework you don’t have to pay the teacher (removal of unwanted outcome). You will complete your homework to save Rs. 100, thus strengthening the behaviour of completing your homework. - Positive Punishment refers to an unfavourable consequence or response following behaviour which leads to a decrease in that behaviour. For example, every time you come late (behaviour), you are slapped (consequence). This consequence of being slapped will demotivate you from coming late, thereby weakening the behaviour.
- Negative Punishment: also known as punishment by removal, occurs when a favourable event or outcome is removed after a behaviour occurs. For example, every time a child wakes up late (behaviour) in the morning, his video game is taken away from him (consequence) for that day. This taking away of the video game following an undesired behaviour results in a decrease in that behaviour.
Note about Operant Conditioning Tools:
Here the terms positive and negative are not used in their popular sense, but rather: positive refers to addition, and negative refers to subtraction.
What is added or subtracted may be either reinforcement or punishment. Hence positive punishment is sometimes a confusing term, as it denotes the “addition” of a stimulus or increase in the intensity of a stimulus that is aversive (such as spanking or an electric shock).
In a nutshell:
Operant Conditioning is a type of learning in which a behaviour is strengthened (meaning, it will occur more frequently) when it’s followed by reinforcement, and weakened (will happen less frequently) when followed by punishment.
It is based on a simple premise – that behaviour is influenced by the consequences that follow. When you are reinforced for doing something, you’re more likely to do it again. When you are punished for doing something, you are less likely to do it again.
If you are a mental health practitioner, who would like to learn advanced techniques based on Hypnosis, NLP and Metaphor therapy to use the principle of Operant Conditioning in your therapeutic practice, check out the Cognitive Hypnotic Psychotherapy® Diploma. If you are a coach who wants to upscale his skills and incorporate different types of conditioning to help clients change their behaviours and habits, then you must check out the Cognitive Hypnotic Coaching® Diploma.

