The Human Mind’s First Line of Defense
Imagine the Human Mind, poised like a soldier within the Human Body. It seems that this tiny soldier is out to guard himself against all those things that he does not agree with, irrespective of the veracity of whatever comes upfront.
Nothing is more important to this Mind embodied Soldier than the calm within – it will do anything to preserve the peace and tranquillity of the mind even if it amounts to proving the other wrong at any cost.
This operational system of fighting and surviving (the so-called opposing or disturbing elements) of the Human Mind is called Defense Mechanism.
What exactly is a Defense Mechanism?
Defense Mechanisms are strategies that are employed by the unconscious mind to effectively manipulate situations, events, and people in a way that safeguards their own sense of well-being, escaping any kind of stress or undue discomfort that the system is not willing to or able to handle.
To quote Anna Freud, the youngest child of Sigmund Freud, Defense Mechanisms are “Unconscious Resources used by the ego to decrease internal stress ultimately, that are devised by people to decrease conflict within themselves, specifically between Super Ego (Conscious Morality) and Id (Instinctive Demand)”.
We shall learn more about Id, Ego & Super Ego in the sections below.
How the Defense Mechanisms work?
Let us look at a few examples to understand how the Defense Mechanisms work.
Example 1: A student who fares badly in school tests blames the teacher for not teaching him well instead of taking on the responsibility of not putting the required kind of input into his work. Here, the student understands that taking the onus of the poor performance on self, will only lead to frustration and a sense of shame. This will increase the stress and harm his sense of self.
So, he unconsciously uses the defense mechanism of shifting the blame on the teacher for his poor performance, which many are not entirely true.
Example 2: An officegoer comes home from work only to scream at his wife for not keeping his clothes in the right place. This is because his boss has reprimanded him for his poor upkeep of official records in the day. So, since he could not retaliate and express his anger and frustration to his boss, he came home to release his stress on his wife to maintain his mental and emotional equilibrium, which had got disturbed because of his boss.
Hence, it will be safe to say that the Defense Mechanism is the mind’s way of maintaining its sense of homeostasis, even if it means manipulating reality.
Role of Defense Mechanisms in Psychology
Occasionally, we encounter individuals who exhibit certain behaviour patterns repeatedly. While some of these behaviours are adaptive and beneficial, others may appear maladaptive or counterproductive.
These habits extend beyond mere actions; they can also encompass thoughts and emotions. Often, these patterns serve as anchors during stressful or challenging situations.
We all employ various defense mechanisms to navigate our daily lives.
At any given moment, the three aspects of the mind—the Id, Ego, and Superego—work in tandem, creating internal struggle and tension. This dynamic often triggers defense mechanisms in our thoughts, emotions, or behaviours as a form of self-protection.
The activation of these defense mechanisms indicates an underlying threat to one’s self-esteem or sense of self. Essentially, these mechanisms strive to shield and even restore the self when faced with potential harm.
Core Concepts from Psychoanalysis to understand Defense Mechanism
To understand the Defense Mechanism, we need to understand the Ego, Superego, and Id as proposed by Sigmund Freud’s theory of Psychoanalysis.
Psychoanalysis theory explains the way the human personality is organised and what are the many facets of its development. Though it was proposed first by Sigmund Freud, it has undergone many changes ever since. As per Sigmund Freud, the human personality is a result of the three structures of the mind.
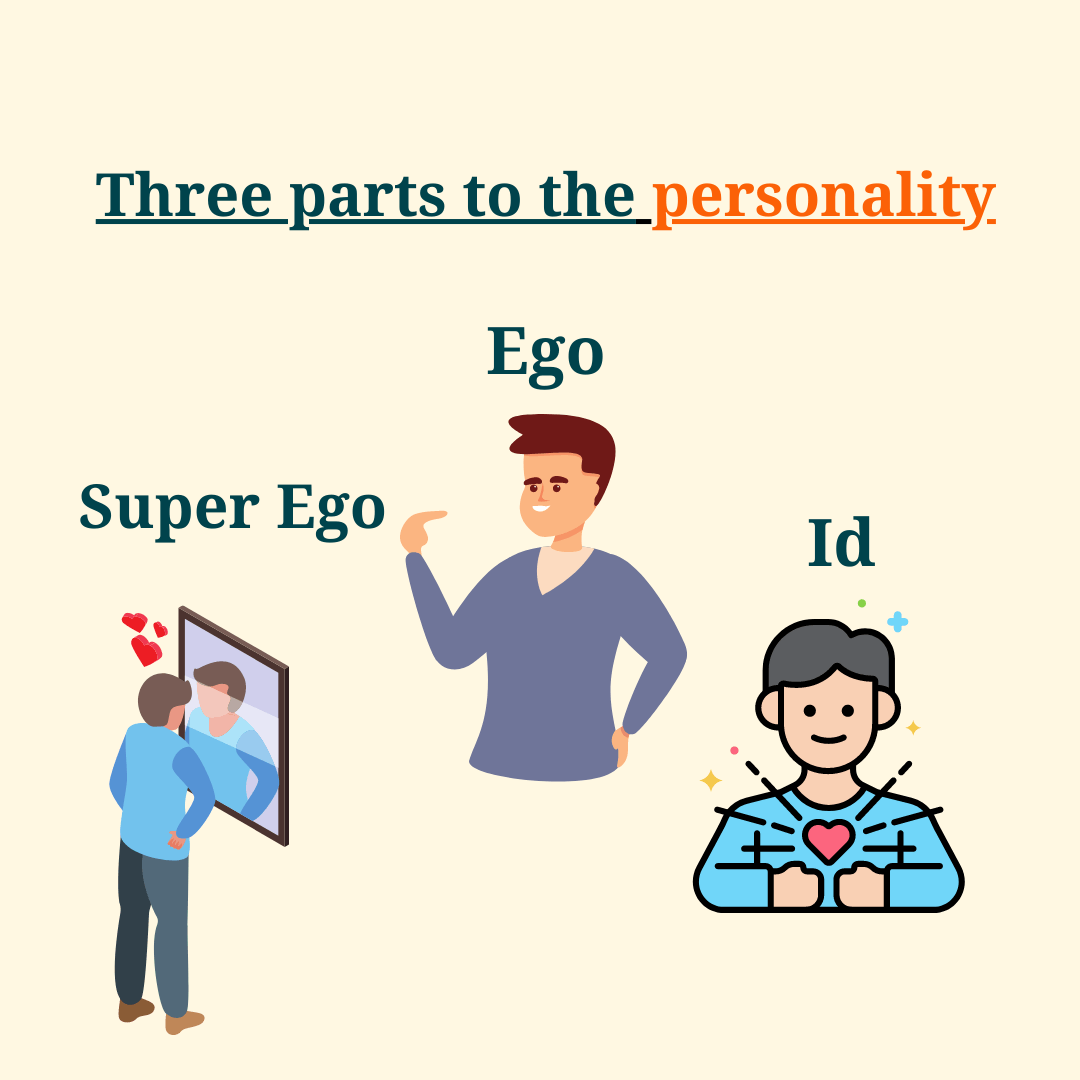
- ID is the innate component that surfaces in instinctive behaviours and is responsible for survival. It is based on the pleasure principle and demands an instantaneous response. E.g., a child wanting a toy.
- EGO is another component of the human mind that surfaces in conscious and appropriate behaviour. It is based on the reality principle and is not instantaneous, but by compromise, it has the power to outweigh the Id. For example, the child reasons that getting a toy will be possible only when one goes to the market.
- SUPEREGO is the last component of the human mind that surfaces again as the voice of conscience and is based on the morality principle. It is the opposite of ego and puts the interests of others before the self. For example, the grown-up child thinks of not insisting on something and being empathetic towards the situation of the other.
So, as we have already understood above about the three important structural aspects of the mind:
Id – About basic needs, impulses, and desires to the extent of being hedonistic about pleasure
Ego – About rationalising the unrealistic demands of the Id and keeping it in check
Super Ego – About moralising the realisation of the demands of the Id by the ego in the paradigm of the rules, regulations, ethics, and morality it possesses
Different types of defense mechanism
As we have understood above, Defense Mechanisms are ‘Ego Protectors’. They are psychological strategies that are used to alleviate any kind of potential danger to the self. Here is a list of the different types of defense mechanisms and their operational characteristics.
| S.No. | Name of the Defense Mechanism | Manner of Manifestation | Example |
| 1 | Denial | Refusal to accept reality | Denying / Not accepting the loss of a loved one |
| 2 | Repression | Called ‘Motivated Forgetting’ where one refuses to remember something undesirable and avoids it consciously | Wanting to harm someone wrongly but pushing it away out of the conscious mind- comes out as other forms of stress like irritability, stress |
| 3 | Projection | Called ‘Outward Displacement’ where the person makes it appear that the other person exhibits certain traits that they possess but refrains from accepting them | One partner in a relationship screams at the other, suggesting that the other person screams at them in any given situation. |
| 4 | Displacement | Directing one’s impulses onto another subject and not the actual one because it may be unacceptable/impossible to do so | Very often, people lose their temper on pets and small children to release the stress they have with someone else |
| 5 | Regression | Reverting or moving back in time to an earlier pattern of behaviour to respond to a stressful situation | Adults start to throw things when facing unmanageable stress or begin whimpering and cooing like a baby to attract attention in the face of stress |
| 6 | Sublimation | Also called Constructive Displacement, wherein one’s unacceptable feelings find a way through positive, constructive | Many artists, like poets, writers, and painters, express themselves through the beauty of their creative works |
| 7 | Rationalization | Creating conscious reasoning / making excuses by cognitive distortion of facts just to prove oneself right | Giving an excuse/ logical reason to the other for harmful behaviour, thereby justifying the act |
| 8 | Reaction Formation | This is a step ahead of denial, which not only includes rejecting the fact but also getting angry with a person who disagrees with their reaction | Not only rejecting that the reason for poor performance was the person’s fault but also directing angst towards anyone who tries to dispel this theory |
| 10 | Introjection | This is observed when the individual starts imitating another person to manage the challenging situation. | When a widow starts emulating her husband in terms of his traits and behaviour to face adversity in his absence. |
| 11 | Identification with the aggressor | Generally observed when a victim of abuse starts mirroring the abuser’s traits just to blur the line of difference between the two to minimise suffering | When an abused partner in a love relationship cooperates with the abusing partner to reduce the aggressor’s anger and minimise the pain |
| 12 | Magical Undoing | Going back to a past event or situation and reliving and reimagining it in ways that could have had a much better outcome to prevent oneself from feelings of guilt and repentance | Thinking /wishing to have studied harder for the exams while having had enough time to study |
| 13 | Compensation | When one tries to fill all those gaps or make up for whatever they think is lacking in oneself to deal with the flaw (which may be real or imaginary). Sometimes this compensation gets too unreal and over the top to an unhealthy extent. | A typical case of people who feel they are too fat and look unacceptable as per societal standards, and they compensate for this by starving/throwing up after eating |
| 14 | Splitting | This happens when the world is perceived as either good or bad as per what the individual perceives. This polarity in thinking styles is replete with immaturity and lacks understanding of the world around as real and a mix of both | Obsessive relationships where the active/ passive controller in the relationship finds the other good or bad as and when the requirements are met |
| 15 | Suppression | A conscious and voluntary effort to avoid anything that is undesirable or unpleasant | Avoiding those memories that contain painful moments with a relationship and trying to distract oneself by pushing them away |
| 16 | Conversion | Transformation of psychological distress into physiological symptoms like blindness, loss of voice, and paralysis despite there being no clinical proof of it | Due to extreme shock, she lost her voice |
| 17 | Dissociation | When the individual consciously does not respond to a stressful event, situation or person and integrate it onto their consciousness | While reliving a particular event in the past of getting molested, the individual starts breathing deeply to accept it and integrate it into their understanding. |
| 18 | Isolation | The act of creating a mental barrier around disturbing thoughts so as not to have any association with them – shows signs of leaving the topic in between, purposeful distraction to something else, and leaving unfinished sentences. | When talking about an unpleasant episode, the son stops the conversation and, after a pause, starts a new conversation. |
| 19 | Intellectualization | The individual focuses on the intellectual components of a situation to distance themselves from the associated emotional stress. This can involve excessive use of abstract thinking or making generalizations to avoid confronting the emotional impact of a stressful event. | When diagnosed with a serious illness, the person begins to research extensively about the medical details, statistics, and treatment options, discussing these in depth with friends and family without addressing their own fears and emotions related to the diagnosis. |
Conclusion:
So, as we can see above, the first line of defense of the human mind is the defense mechanism. They are a way of life and make it possible for us as individuals to stay sane and safe to a certain extent by not immediately reacting to challenging times.
The function of the Defense Mechanism can be likened to the circuit breaker in our home electricity boards, which often does the favour by breaking the electric circuit to relieve itself from the overwhelming load and thereby preventing damage to the other electrical appliances.
Similarly, Defense Mechanisms break the circuit of a nonstop flow of thoughts and feelings and behaviour by purposefully resorting to another survival strategy to buy time to empower oneself to tackle the challenging situation.

However, having said that, once the defense mechanism overextends its limits and starts dominating the normalcy of life, one needs to seek professional guidance and mentor to be able to recognise and address the real issue at hand that is a threat to the self-esteem and self-concept at a particular point.
This not only restores our original state of mind and self but also has an empowering impact on our new learnings.
If you are a psychologist who would like to learn how to help your clients develop healthy self-belief and overcome dysfunctional defense mechanisms, check out this comprehensive program that integrates the different approaches to psychotherapy.

