When we talk about what is hypnosis, we often tend to be either talking about: the relaxed, focused, absorbed feelings associated with a ‘trance state’, or we tend to be talking about the fascinating things people can do when hypnotised: such as not feeling pain, or experiencing hallucinations.
Some scientists define hypnosis as an “altered state of consciousness” marked by changes in the way the brain functions. Others believe that hypnotised participants actively motivate themselves to behave in a hypnotic manner and are not simply responding to suggestions. Therapists sometimes define hypnosis as a process to access the contents and resources of the subconscious or as some call it the unconscious mind.
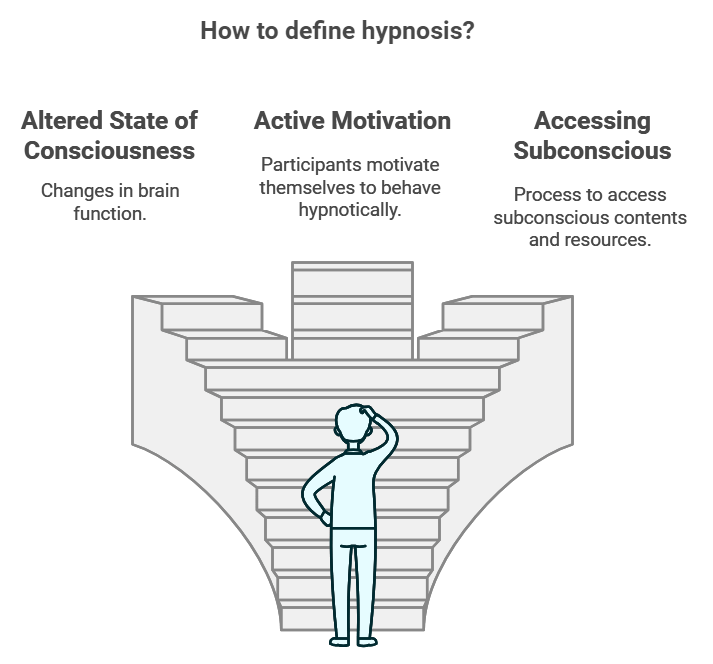
Like the story of the blind men and the elephant, it is possible that these explanations all describe different parts of the phenomenon of hypnosis.
What is Hypnosis?
Frequestly Asked Questions about Hypnosis
Is Hypnosis Real?
Yes, hypnosis is indeed real, supported by scientific evidence and extensive research. Multiple studies have shown its effectiveness in various fields of application.
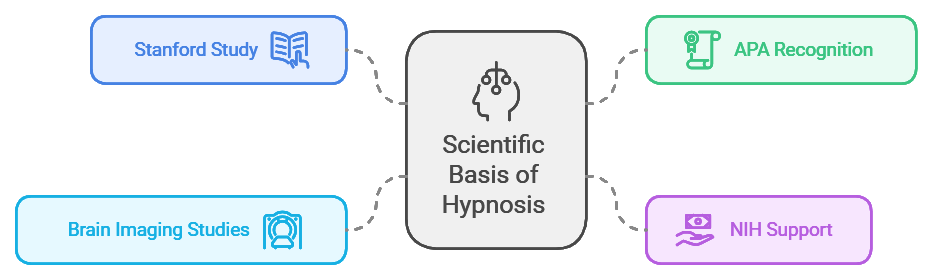
Let’s explore the scientific basis behind hypnosis:
- Stanford University School of Medicine Study: Researchers at Stanford University School of Medicine, led by David Spiegel, MD, conducted a groundbreaking study on hypnosis. Their research demonstrated how hypnosis can effectively reduce pain and facilitate therapeutic improvements. The findings support the reality of hypnosis as a powerful tool for altering perception and controlling the mind and body.
Citation: Study identifies brain areas altered during hypnotic trances. (2016, July 28). News Center - American Psychological Association (APA) Recognition: The American Psychological Association recognizes hypnosis as a valid therapeutic technique. Numerous articles and studies published by the APA highlight the scientific foundation of hypnosis and its successful implementation in areas such as smoking cessation, weight management, anxiety reduction, and more. This recognition further solidifies the legitimacy of hypnosis as a proven therapy tool.
Citation: American Psychological Association (APA) - National Institutes of Health (NIH) Support: The National Institutes of Health acknowledges hypnosis as a valuable complementary and alternative medicine practice. Through funding and support, the NIH has contributed to research on hypnosis, particularly in pain management and behavioural health. Their endorsement reinforces the scientific underpinnings of hypnosis and its efficacy in various contexts.
Citation: Hypnosis. (n.d.). NCCIH - Brain Imaging Studies: Sophisticated brain imaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), have provided valuable insights into the neurological mechanisms of hypnosis. These studies demonstrate observable changes in brain activity and connectivity during hypnotic states, confirming the physiological effects of hypnosis.
Citation: Wolf, T. G., Faerber, K. A., Rummel, C., Halsband, U., & Campus, G. (2022, January 13). Functional Changes in Brain Activity Using Hypnosis: A Systematic Review. PubMed Central (PMC)
Is Hypnosis Natural? Can anyone be hypnotized?
The best way to answer these questions is by recognising that we have all experienced hypnosis and that it is a naturally occurring state.
Surprised?
It is true. In fact, we experience hypnosis multiple times a day.
If you have ever been so engrossed in a movie or a book that you felt moved by it, or that your emotional state was influenced by it, then you have experienced a hypnotic state.
If you have ever told yourself that I wouldn’t be able to do something and when the time came to do it, you weren’t able to do it, you have been in a hypnotic state.
Or if you have ever told yourself I can do it and when the time came to do it, you automatically felt this surge of confidence, you have experienced a hypnotic state.
or if you have ever been to a supermarket to buy ketchup but by the time you reached the counter you had picked up a lot more than just ketchup, then you have been in a hypnotic state.
In short, Hypnosis is a natural & universal human trait. Each one of us, in some form or the other, experiences hypnosis on a daily basis.
It may even be argued that we live most, if not all, of our lives in different types of hypnotic states.
Which also means that everybody is hypnotizable. As long as the person is willing, he or she can experience a hypnotic state.
What happens in Hypnosis and How does Hypnosis feel?
During hypnosis, you will generally remain conscious of your surroundings.
Some of the sensations you may experience when in a hypnotic state include:
- Tingling in your fingertips or limbs
- A sense of numbness or limb distortion
- A sense of being light and floating away from your body
- A heavy feeling like you are sinking
- A sense of energy moving through your body
- Feelings of emotions
- Fluttering eyelids
- An increase or decrease in salivation
It is important to remember that these are just some of the examples of sensations that you may experience.
In reality, you can actually experience any other sensation that the hypnotist suggests for you to experience.
How does one know whether he or she is hypnotized?
The discovery of hypnosis has led to three different theories on What is hypnosis namely role theory, altered-state theory, and dissociation theory.
Whether or not you believe that hypnosis is an altered state of consciousness (i.e. altered-state theory), the key characteristic of hypnotic responding is involuntariness.
This is known as the “classic suggestion effect” by André Muller Weitzenhoffer, who was one of the most prolific researchers in the field of hypnosis in the latter half of the 20th century.
When a subject carries out a hypnotic suggestion, they experience the behaviour as happening all by itself, involuntarily.
For example, if the suggestion implies that the subject’s arm is rigid like a bar of iron, the classic hypnotic experience is that the person’s arm truly becomes rigid, on its own, without deliberately holding it stiffly.
While attempting to experience hypnosis, it is important to remember the following things:
- When you notice that you are noticing these sensations, do not become alarmed or you may shock yourself right out of the hypnotic state.
- Don’t try too hard to get into a hypnotic state, just expect the hypnotic state to occur gradually and it will.
- Suggestions stay with some individuals indefinitely, others need reinforcement.
- The effects of hypnosis are cumulative: The more you practice the techniques and incorporate posthypnotic suggestions, the more permanent the results become.
How does Hypnosis Work?
In order to understand the what is hypnosis and how it works, one needs to understand the model of mind and the functions of the different parts of the mind. You can checkout the video titled “Model of Mind” on the ICHARS Youtube Channel.
What are the different applications of Hypnosis?
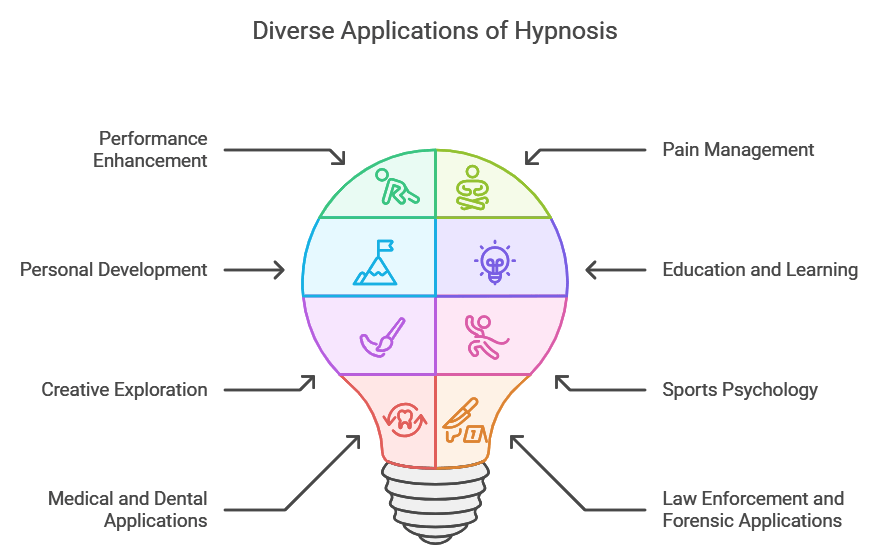
Hypnosis, primarily known for its applications in therapy and coaching, researchers have also explored its use in various other domains like:
- Performance Enhancement: Boost confidence, overcome anxiety, and improve focus in sports, public speaking, acting, music, and competitive endeavors through suggestion and visualization.
- Pain Management: Reduce discomfort during medical procedures, dental work, childbirth, and chronic pain conditions by modifying pain perception and enhancing coping mechanisms using relaxation and suggestion techniques.
- Personal Development: Facilitate personal growth, behaviour modification, and self-improvement. Overcome fears, build self-esteem, overcome bad habits, enhance motivation, and achieve personal goals.
- Education and Learning: Optimize memory retention, study skills, and learning abilities through techniques like accelerated learning, focused concentration, and addressing test anxiety.
- Creative Exploration: Unlock creativity, overcome blocks, and enhance brainstorming sessions through hypnosis, stimulating artistic expression, and expanding imaginative potential.
- Sports Psychology: Develop mental toughness, improve focus, concentration, and visualization skills to achieve peak performance states in sports and athletics.
- Medical and Dental Applications: Alleviate anxiety, modify behaviours, manage symptoms, and improve patient well-being through hypnosis in medical and dental treatments, including preoperative preparation, anesthesia assistance, and conditions like IBS or teeth grinding.
- Law Enforcement and Forensic Applications: Helping criminal investigations through forensic hypnosis, assisting in retrieving memories or crime details from victims or witnesses.
- Personal Exploration and Past-Life Regression: Explore past-life experiences or access early childhood memories through hypnosis, offering a subjective and esoteric perspective.
- Advertising and Marketing: Using hypnotic language patterns, persuasive suggestions, and subconscious priming in advertising and marketing campaigns to influence consumer behaviour and enhance brand engagement.
- Content Writing and Copywriting: Captivate readers, evoke emotions, and convey messages effectively by incorporating hypnosis principles into engaging and persuasive written content.
- Journalism and Interviewing: Establish rapport, encourage deeper responses, and facilitate detailed recall from interviewees through hypnotic language, pacing, and leading techniques, creating a relaxed and comfortable atmosphere.
- Negotiation and Persuasion: Enhance persuasive abilities in negotiation scenarios by employing hypnotic techniques such as rapport building, establishing anchors, and utilizing persuasive language patterns to influence the subconscious mind and appeal to emotions.
- Leadership and Management: Inspire and motivate teams, boost morale, and enhance performance by applying hypnosis principles like guided visualization, positive suggestion, and anchoring.
- Entertainment and Stage Hypnosis: Engage audiences with interactive stage shows that hypnotize participants, combining suggestion, showmanship, and participation to create a hypnotic entertainment experience.
While hypnosis can be effective in these domains, it is essential to approach its application with caution and seek guidance from trained professionals.
What are the different career options after learning Hypnosis?
- Hypnotherapist or Hypno-Counselor
- Hypnotic Coach
- Subject-matter Expert
- Entertainment Industry
- Supportive services
- Sales
- Human Research
- Training and Development
Do check out our more detailed post on career options after hypnosis if you’re interested in exploring how hypnosis can be applied in each of these fields.
What is Hypnotherapy and Hypnotic Coaching?
Hypnosis practitioners commonly apply hypnosis in the field of change work. They combine hypnosis with various coaching models and therapeutic approaches to help clients in achieving their goals and overcoming intense emotional issues in a more natural, effective, and sustainable manner.
Hypnotherapy is the popular term for the application of hypnosis in therapy, while Hypnotic Coaching is now the preferred term for its application in coaching.
Quick Summary of What is Hypnosis?
So there you go, hypnosis is not magical or mysterious when you know the true facts. It is simply a state of hyper-receptivity and includes a group of techniques for focusing the mind so that the unconscious can absorb pre-agreed suggestions, in order to facilitate change.
However, the reality about “what is hypnosis” has been bent and distorted by sensationalism.
This is a pity because not knowing this, can and probably does, prevent many people from trying it for the first time.
Remember, that it is perfectly safe so you have nothing to lose. In fact, hypnosis can help you unlock a world of possibilities for personal growth, change and improvement.
If you are a mental health practitioner, you can greatly benefit by learning more about what is hypnosis and how to integrate it with different therapeutic techniques like CBT, REBT, Mindfulness, Behavioural Therapy, NLP and Psychoanalysis. Check out our comprehensive eclectic course titled Cognitive Hypnotic Psychotherapy for mental health practitioners.
If you would not like to work with intensely emotional issues or traumas but limit the use of hypnosis towards Coaching, be it life, relationship or executive, do check out our Diploma Program on Cognitive Hypnotic Coaching.

